In the Cost Management + Billing service blade > Cost analysis > there’s a possibility for filter after tag and if the environment like dev, Prod has been considered as tag. We can filter here.
Event filter after services.
Enterprise and industry solutions
In the Cost Management + Billing service blade > Cost analysis > there’s a possibility for filter after tag and if the environment like dev, Prod has been considered as tag. We can filter here.
Event filter after services.

Topics
Related topics
Each project need a holistic monitor strategy.
Scenario: A financial organization is moving its systems to Azure, with a mixture of IaaS and PaaS services. In its previous environment, the organization had several instances where systems failed or issues arose. There was an extended delay to engage resources and resolve the issues. This situation affected customers’ ability to access their accounts, and it influenced satisfaction.
The organization wants to design a monitoring strategy that encompasses all the solutions that it uses. There should also be insights and alerting into the accumulated log data. The organization wants to quickly identify and minimize the impact if systems fail in the future.
Continuous monitoring strategy

Scenarios
Data collected
| Windows (WAD) | Linux (LAD) |
|---|---|
| Windows event logs | Syslogs |
| Performance counters | Performance counters |
| IIS logs | Log files |
| Application logs | |
| .Net eventsource logs | |
| Manifest based ETW logs | |
| Crash dumps log | |
| File based logs | |
| Agent disgnostic logs | |
Sources
| Azure Diagnostics Extension | Azure Log Analytics |
|---|---|
| Only Azure VMs | Azure/other clouds/on-prem VMs, |
| Sends data to azure storage, azure monitor metrics (only win), and event hubs. | collects data to azure monitor logs. |
| is required for solutions, azure monitor for vms, azure security center, und… |
Coming soon…
Coming soon…
Coming soon…


Sources
| Alert state | Description |
|---|---|
| New | Issue has been detected but has not been reviewed. |
| Acknowlaged | Administrator has reviewed the alert and started working on it. |
| Closed | Issue has been resolved. |
NOTE : The state changes are stored in alert’s history.
Alert states are independent of Monitor condition (fired or resolved).
We can use the Role-based access control (RBAC) at different levels
The RBACs which are available for Azure Monitor service are the following:
Ex. A user with the Monitoring contributor access for VM1 can only consume and mange the alert that have been generated for VM1.
Alerts are defined via Azure Minitor Service blade.
Go to Azure portal > Monitor service> Go to Alerts section > Use add alert rule button.
According to the seleced resource there’s different signals available.
Signal types
The alert configuration is different respectively. But without considering the signal types always we need the following items for creating an alert rule in Azure Monitor Service.
| Resource (For the scope of Alert Rule) | The scope of alert is specified in this step. – Subscription level – Resource Group level – Region – A specific resource – One Alert Rule for multiple resources with the same Resource Type is available. |
| Condition | The monitoring criteria. |
| Action Group | Collection of notifications. |
You owe your dreams your courage.
Koleka Putuma
In Azure Subscription features:


The list of all resources providers/ all available resources is listed.

Topices

Hybrid identities
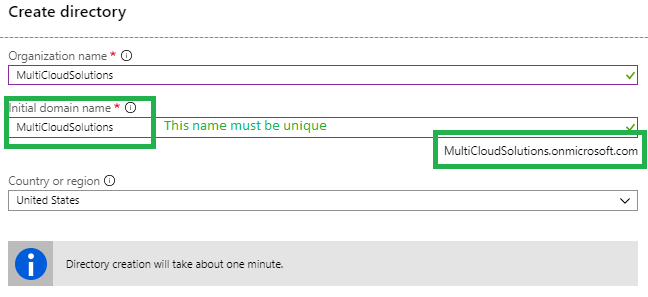
Create Azure Active Directory (Azure Portal > All Services > Create button > the following image)

Users
Groups
Enterprise applications: add new SaaS applications like Box, Dropbox,…
Devices: to mange devices.
App registration: Register application to machine to machine communication / client credential flow [more].
Application proxy: for exposing on-premises.
Azure AD Connect: for sync with on-prem Active Directory to AAD for hybrid identity.
App registration blade features are:

New Registration

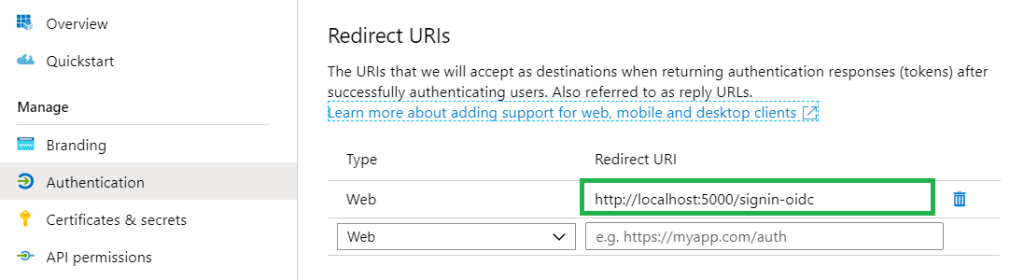
Web APP/API is like a web site. The URL infront of Web APP/API (REST API) is the Sign-on URL. Ex. http://localhost:5000/signin-oidc
Native is like mobile app, desktop application or javascript single-page application. Redirect URL is where Azure AD directs the authenticated user’s details.
After the app registration, the following items can be important for developers. They are always available on the registered app blade.
How to go the registered app blade
AAD > App registration> select & click the registered
Application/ Client ID
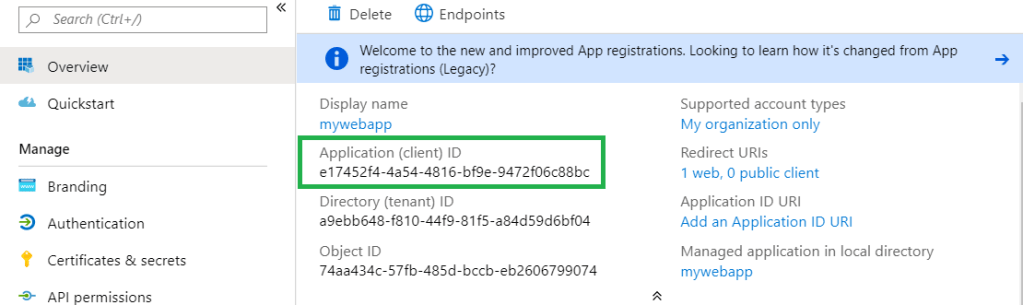
Redirect URL after successful authentication
Logout URL

App Registration usages
Licenses
Required license for conditional access policy
Conditions
The conditional access policy uses the Sign-in Risk value (it’s a probability). But it’s not the only value. Based on the policies different probability values have to be calculated [more]. Based on how conditions are configured different values are calculated and used.
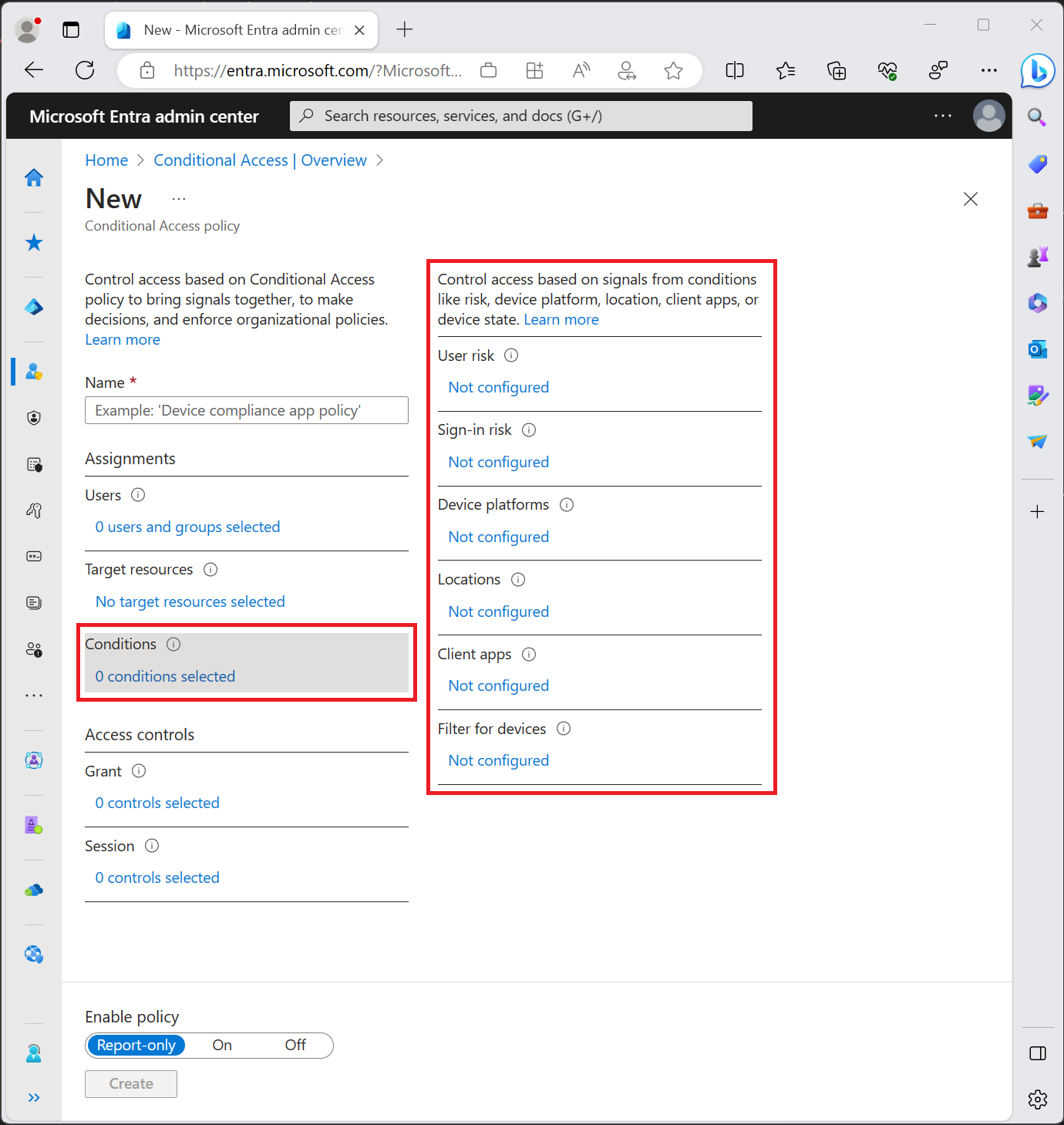
Grant
In Grants either you block the users who have the conditions or you grant then if one of the checkboxes is available. Multi-factor is available only in the following licenses but with some differences [more]:

Report-only mode [more]
Report-only mode is a new Conditional Access policy state that allows administrators to evaluate the impact of Conditional Access policies before enabling them in their environment. With the release of report-only mode:

Source : https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/conditional-access/overview
You owe your dreams your courage.
Koleka Putuma
| Disadvantage of Active Directory If a company has use the Active Directory of the authentication and the personals are allowed to do home office, therefore they need to use VPN Connection to authenticate to the company’s Active Directory. This isn’t so secure. |
Classic active directory cannot manage modern devices with the following features:
What can help us to manage the modern devices:
WS-Federation
It’s a redírect-based flow. we go to a site and site says we are anonymous, and it redirects us to a authentication provider.
The user can pick an authentication provider and we provide the credential and then we get SAML post back.
SAML looks like XML and it contains what they call a SAML assertion and that establish your identity.
SAMLp
More flexible and supports more structured way to do SAML, more attributes.
OpenID Connect
OpenID Connect & OAuth are not synonymous.
OAuth is about a delegation protocol. For example I say, I’m allowing you to access my application if you match certain criteria. In this case I don’t know about the identity but if you have brown eyes and brown hairs, you are allowed to work with my software.
OpenID Connect says that you have to have minimum set of protocols that also establish your identity. OpenID is not only for web / mobile application. It can be applied to anything.
The following figure demonstrates the OpenID Connect usage for Web Application.
Insert photo here!
Single Page Application is typically written in JavaScript (OAuth 2.0 Implicit Flow). Using OAuth 2.0 implicit flow and Single Page Application don’t have a secure way of storing long-lasting refresh token.
In OAuth 2.0 implicit flow, we assume that with closing the browser the user is logged out. Therefore OAuth 2.0 is suitable for Single Page Application.
Like the applications running on a Mac OS, Linux OS or Windows OS, we use the Authorization Code Grant Flow. Here we have capability of storing long-lasting refresh tokens in a secure, encrypted manner offline.
| Azure AD V1 endpoint | Authorization Code Grant Flow It has used authorization code grant flow for mobile apps and desktop applications as well. |
| Azure AD V2 endpoint | Authorization Code Grant Flow It prefers not to use authorization code grant flow for mobile app but only for desktop applications. Proof of key exchange (PKCE) flow It’s for mobile application. |
| Web Browser talks to Web App It can be developed with WS-Federation, SAMLP, OpenID Connect. | Sigle Page Application talks to Web API It can be developed with OAuth to implicit flow, so ADAL.JS, MSAL.JS. | Native App talks to Wen API |
| Web Application talks to Web API It uses user credential delegated credentials, or using application’s identity. | Daemon If there’s no authentication opportunity. Daemon can call API registered in Azure AD. |
Create a .Net core MVC project via the PowerShell.
# Create .NetCore MVC Project
$ProjectName="DotNetCorePipeline"
cd C:\YOUR PATH\AuthenticationForDevelopers
new-item -Name $ProjectName -ItemType directory
cd C:\YOUR PATH\AuthenticationForDevelopers\$ProjectName
dotnet new mvc --auth SingleOrg --client-id YOUR CLAINT ID --tenant-id YOUR TENANT ID --domain YOUR DOMAIN NAME --no-https
After creating the project go to project folder and open the project file in Visual Studio and run the project. [More Info about ID Tokens]
for scenarios, in which the external users are the focus.
SQL resources are the following SQL database, SQL warehouse and SQL server. The authentication is possible via AD.
It’s via power shell and API management Rest API possible.
The developers can export the API definition in OpenAPI JSON format and WADL from API Management Developer Portal.
And the developers can use these files to generate client-side code by using the tools, which is adequate for them such Swagger codegen or Postman to start calling the API in a short time.
Azure Portal > API Management > Select the API Management Instance > APIs > Developer Portal Button > APIs Tab in Developer Portal > Select an API > We see the list of APIs Actions/Operations > Select an Action > API definition button -> Download the OpenAPI 3/ 2 JSON or YAML format or WADL.
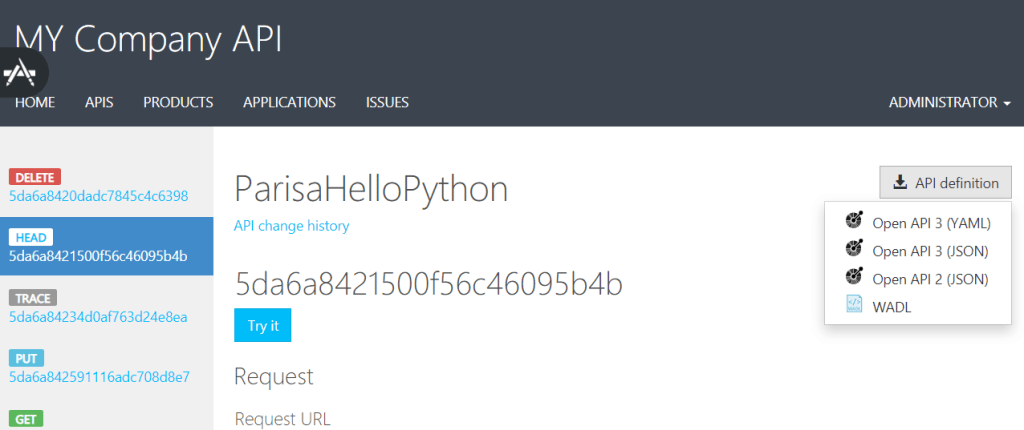
Definition
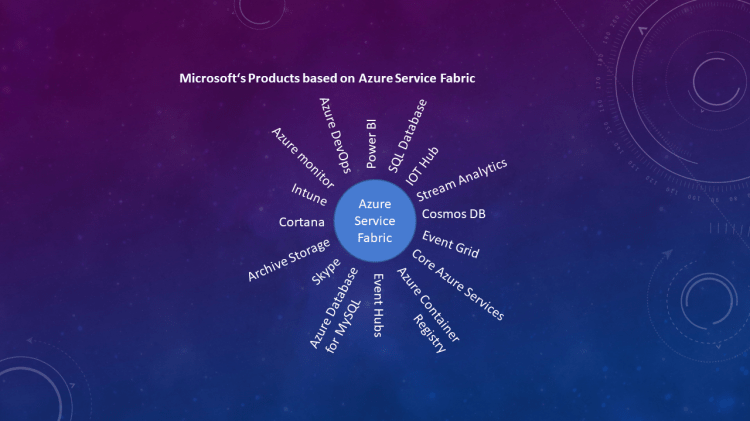
Azure provides App Services through Azure Service Fabric. This abstracts the serviaces and underlying resources through the app service.

When and why we should use it?
Unique capability of each App Service
| App Service | Description |
|---|---|
| Web Apps | – is used to host web application. |
| API Apps | – is used to host APIs. |
| Mobile Apps | – is used in scenarios where mobile devices occasioonally have internet connectivity. – Backend for mobile applications. – Supporte push notifications. – And ability to work offline. |
| Logic Apps | -They orchestrate APIs into business process. – Create a complex workflow to automate a business process. – And calling APIs, which are anywhere. – |
| Function Apps | – is used to response to events. |
All the above App Services can fit together.
Resources
Related words for the Service Fabric in Microservice Architecture:
Microservices Development possibilities on Azure Cloud:
| Azure Function | Kubernetes Service | Azure Service Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| – They are micro-microservices. – reactes to an external change & event arrived on service bus. E.g. Blob created, message arrived on a queue or service bus queue. – They can be called as REST service from another application. – Azure function & Serverless computing is a great choice for types of applications that response to some events. – Good alternative for ASF (Azure Service Fabric) and AKS (Azure Kubernetes Service). – Doesn’t need infrastructure at all. – Suitable for background tasks with some upfront design. | – Microsoft implementation of open-source container orchestrator based on Docker => Docker Container – Container is faster => lighter virtual machine – Run Docker Container on Azure=> to manage environment (Upgrade, scale, versioning, expose network, load balance, and …) – Docker is a technology to manage and run multiple containers in production. -Azure supports Kubernetes natively & no installation need. | – Similar to containerization technologies. – Focuses on Microservices. – Kubernetes solves all the problem and developer should only develop the services-> it’s not easy to write scalable application, which runs on multiple & distributed clusters. – Container orchestration => Microserrvice Challenges: – Service Communication => service and instances of the services. – Service Discovery => How to talk to another Microservices, when there’s thousands on instances. – Monitoring Application => telemetry and collecting logs, provisioning and upgrading microservices. – Testing locally – Managing and recovering from downtime. – Scaling in & out. |
Programming model of Azure Service Fabric:
| Reliable Service: They are like windows services or Linux daemon application. It’s like console application. These services divided to sub types: – Stateless Services – Statefull Services -> for co-locate compute and data. | Reliable Actors: It uses the Virtual Actor Design Pattern and built on state-full reliable service framework. For massive amount of requests. |
| Guest executable: for existing projects without charging too much. | Containers: is like quest executable and still run on the Host OS and is completely isolated piece of deployment. |
Advantages of State-full Services:
Entry point from outside to back-end application is as follows:
| Web API – has no state (Stateless Service) – Must scale | Microservice – Independent part of the business logic and is perfect for Actor model. |
Advantages of Stateless Services:
Start to work with the Azure Service Fabric:
Normal APP vs. Reliable APP
| Normal App | Reliable App |
|---|---|
| – An Application – Easy to write (Established framework) – Great choice of libraries – No learning curve | – A reliable service – Easy to write (established framework) – Reliable service is like an exe file that can be run without service fabric. – Great choice of libraries (x64 only) – None to little learning curve – Access ASF API for microservice scaling, health reporting, discover other services. – we can use plugable communication model. (They are Azure Service Fabric Built-in) via HTTPS, TCP, Wensocket, Custome TCP – Access to reliable storage, stateful service, low latency, high speed, local storage, replicated across machines. |
References