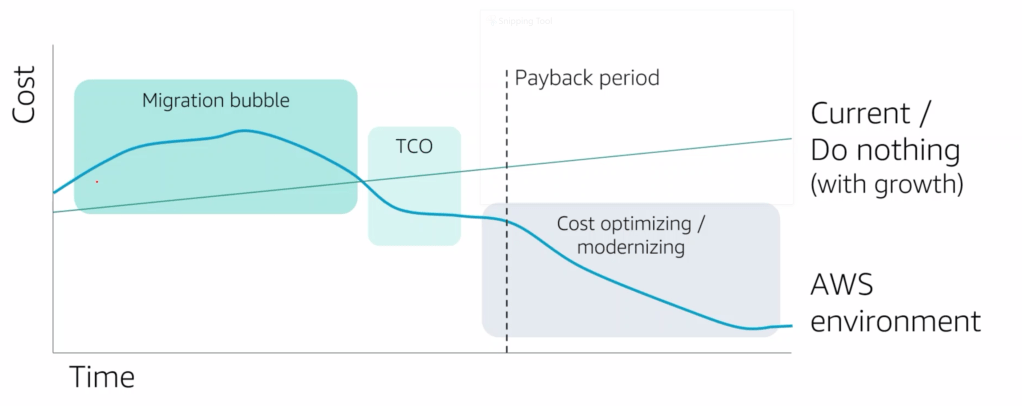
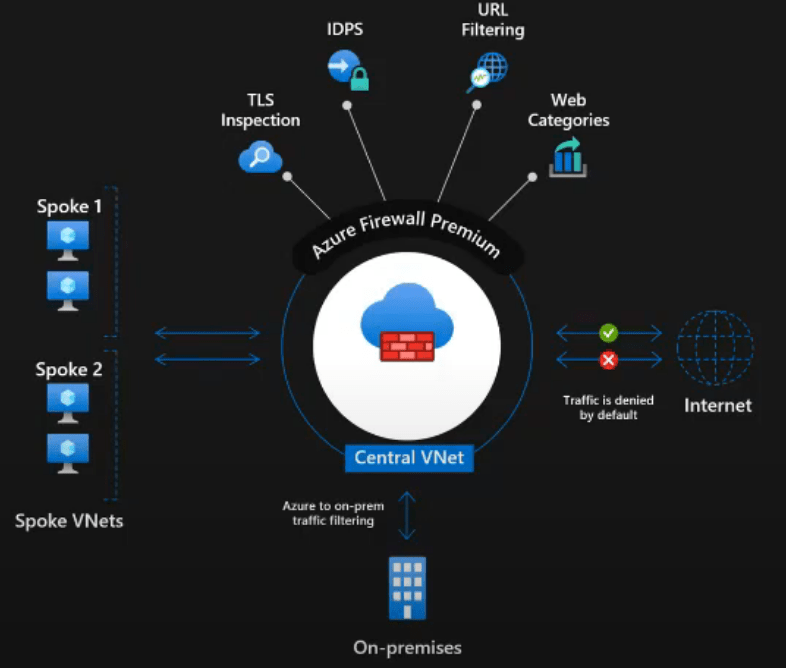
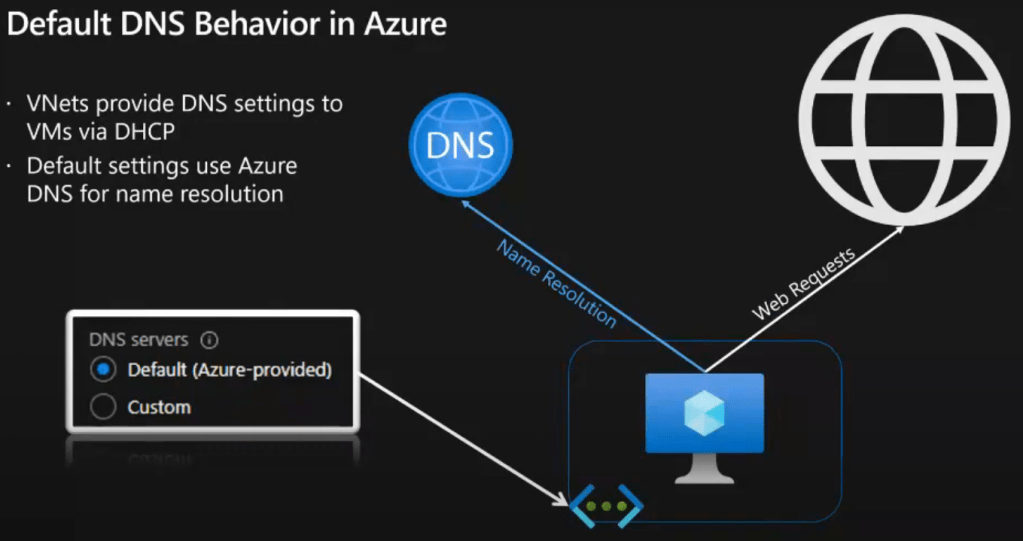
Most organizations choose to work with multiple cloud providers, because it’s a struggle for an enterprise to find only one public cloud infrustructure provider, which meet all their requirements. [refrence]
The following figure demonstrates that the multi-cloud solution is a sub concept for hybrid-cloud computing.

Multi-cloud scenarios
1-Strategic advantages of partitioned complexity
To avoid committing to a single vendor, you spread applications across multiple cloud providers. Best Practice: weight the strategic advantages of a partitioned complexity this setup brings. Achieving workload portability and consistent tooling across multiple cloud environments increases development, testing, and operations work. [1]
2-For regulatory reasons
For regulatory reasons, you serve a certain segment of your user base and data from a country where a vendor does not yet have any presence. Best Practice: Use a multi-cloud environment only for mission-critical workloads or if, for legal or regulatory reasons, a single public cloud environment cannot accommodate the workloads. [1]
3-Choose the best services that the providers offer
For deploying application across multiple cloud providers in a way that allows you to choose among the best services that the providers offer. Best practice: Minimize dependencies between systems are running in different public cloud environments, particularly when communication is handled synchronously. These dependencies can slow performance and decrease overall availability. [1]
4-To have data autonomy
To have data autonomy in the future, therefore companies can take their data with them wherever they end up going.
Advantage of multi-cloud scenarios
- To avoid vendor lock-in. The multi-cloud helps lower strategic risk and provides you with the flexibility to change plans or partnerships later. [1]
- If the workload has been kept portable, you can optimize your operations by shifting workloads between computing environments. [1]
Hybrid-cloud scenarios
Hybrid-cloud description by National Institute of Standards
Hybrid cloud is a composition of two or more distinct cloud infrastructures (private, community, or public) that remain unique entities, but are bound together by standardized or proprietary technology that enables data and application portability. [2]
Cloud and on-premises, which were previously distinct entities and had cumbersome interaction configuration, are now converging to provide more efficient, less costly, and more flexible operation model for workflows.
1-Backup & Archive [2]

2-Data Protection [2]

3-Lifecycle Partitioning [4]
Lifecycle partitioning is the process of moving parts of the application development lifecycle to the cloud while the rest remains on premises. The most popular is the cloud deployment and testing but move to on-premises for the production deployment.
4-Application Partitioning [4]
A part of an application is running in the could and the other part runs on premises. For example, Sony PlayStation runs databases for individual games in the cloud but takes care of user authentication on-premises.
5-Application spanning [3]
Application spanning happens when the same application runs on-premises and in the cloud. “Best Buy” is an example of the application spanning. The entire online store application is running across multiple cloud regions and multiple on-premises data center to allow it to quickly adjust to demand.