- Regions
- Availability Zones (AZs)
- Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs)
- AWS VPC Networking
Regions and Availability Zones allow anyone to create worldwide infrastructure with ease. They also allow for many options for creating redundancy within your platform. By properly using these components, you can create world-class level systems in terms of both scale and reach.

A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a isolated private network that you control within the larger AWS network. These private networks allow you to configure your network architecture the way you desire. A VPC is region specific. You decide if your VPCs connect to each other or if you keep them independent. If you connect your VPCs, it’s up to you to configure them according to regular networking guidelines.
VPC aspects
- Security groups are the same as firewall but not exactly
- Two VPCs can have peering, even if they are in different regions
- One VPC per region has automatically multi-AZ
- AWS create a default VPC in every region but can be deleted
Services in VPC
The instance oriented fetures
- Amazon RDS
- Elastic cache
- Document DB
- Elastic search
- EC2
- Load balancer
- Net Tune
Services not in VPC
Service oriented features and global services that have access to internet
- SQS
- S3
- DymoDb
- SNS
- Cloud front
- SCS
- API gateway
Network Ranges
A network range is a consecutive set of IP addresses.
Network ranges are described using “CIDR” notation. CIDR notation consists of the first IP address of the network range, followed by a “slash”, followed by a number. That number describes how many consecutive address are in the range. A “/24” address has 255 addresses, while a “/16” has 65,536 addresses.
We cannot connect two VPCs with overlapping IP address ranges
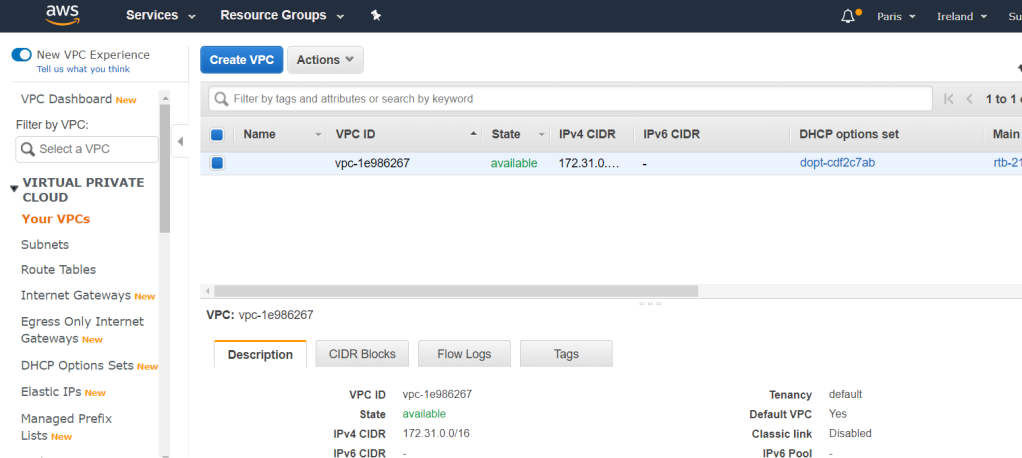
Create VPCs
There are two ways in the AWS management console to create a new VPC.
You can create a very basic VPC by creating a new VPC from within the “Your VPCs” section of the VPC service. This option is best if you are an advanced VPC user and want to customize your VPC completely.

the second way is by using the VPC launch wizard.
Using the “Launch VPC Wizard,” create a new VPC. Select the “VPC with a Single Public Subnet” option. Name the VPC “Lesson-VPC” and keep the default options and create the VPC.
Review the new VPC, the routing tables that were created with it as well as the subnet and Internet Gateway.
Step1: create VPC

Step2: VPC created

VPCs List
The ‘Lesson-VPC’ is my new VPC

Step3: Create subnet

The subnets can be created in any availability zones of the VPC’s region.
Network components

| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Subnets | is tied to Availability Zone (AZ) and all resources created in this subnet are located in this availability zone |
| Route tables | is attached to one or more subnets and can be shared between subnets in different AZ. |
| DNS | |
| DHCP | |
| IPv4/6 | |
| Internet Gateway (Network routing) | is represented in Route Table of the subnet and the services created in the subnet can send traffic to internet with public IP. Internet can send traffic to instances as well. |
| NAT Gateways (Network routing) | Services can send traffic out to internet but cannot receive from internet. |
| Security Group | is a statefull firewall, can attach to EC2, RDS database |
| Network ACLs | Network Address Control List, is a kind of stateless firewall and is applied to subnet. |
Network routing
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
| Internet Gateways | |
| NAT Gateways | |
| No internet connections | is for connecting two subnets in a VPC with each other |
| VPN connections | encrypted connection to connect to on-prem |
| DirectConnection | datacenter to AWS |
Debugging VPC Network
VPC Flow Logs
Flow logs allow you to see higher level network debugging information like the source port and source IP, and destination port and destination IP of traffic flowing within your VPC.
Traffic Mirroring
Traffic mirroring is like traditional “packet sniffing” on specific ports.
Edge cases
- Multicast networking : is not supported in AWS
- Penetration testing
- Running email server
AWS networking does have some limitations that your own data center network would not.
- You cannot use multicast in a VPC
- You cannot put network cards into “promiscuous” mode to sniff ethernet packets.
- There are some restrictions on opening up ports for SMTP
- You cannot have network scans run against your account without discussing with AWS
You can connect VPCs together to enable:
- Cross VPC connections
- Cross region connections
- Cross account connections