- AKS components
- AKS security (service principal or managed identity)
- AKS operation (scaling and autoscaling)
AKS components
I assumed that you are familiar with the Kubernetes Cluster concepts (elementary level). Therefore I didn’t do any deep dive into the elementary components. The focus of this post is the following topics:
- Azure-related Kubernetes components
- Deploying AKS with Terraform
The control plane (Kubernetes core component)
It’s the core of the Kubernetes Cluster and doesn’t matter on which cloud provider platform you are provisioning a cluster. The main OS for AKS is Linux based.
Node pool (AKS component)
AKS has two types of Node pools:
- System Node Pool: contains the nodes on which the control plane is running. For the control plane’s high availability is recommended to have at least 3 nodes in the System Node Pool.
- User Node pool: contains the nodes on which my applications, APIs, APPs, or Services are running. This node pool can have one of the following host’s OSs.
- Linux
- Windows
An AKS Cluster can have both Windows and Linux -based User Node Pools in parallel. We can use nodeSelector in the YAML file to specify on which User Node Pool my application should be deployed. See more in the video below.
Note:
The importance is that all the nodes in a Node pool (doesn’t matter System or User) have the same VM size. Because we can specify one VM size for one Node Pool.
Node components
Each node in the Node Pool is a VM. Kubernetes uses the following components to orchestrate the nodes and pods that are running on the nodes.
- Kubelet: manages deployments
- Kube-Proxy: manages the nodes’ networking
- Container runtime: up and run container images
This video walkthrough the AKS core concept and components and its implementation in Terraform.
The PowerPoint slides of the video are available here.
Shared slides: https://www.slideshare.net/parisamoosavinezhad/aks-components
GitHub: https://github.com/ParisaMousavi/enterprise-aks
For a nodeSelector sample code see the sample YAML file here: https://github.com/ParisaMousavi/solution-11-aks-apps/blob/main/sample-win/sample.yaml it’s a ASP.Net Application that will be deployed on windows node.
AKS security (service principal or managed identity)
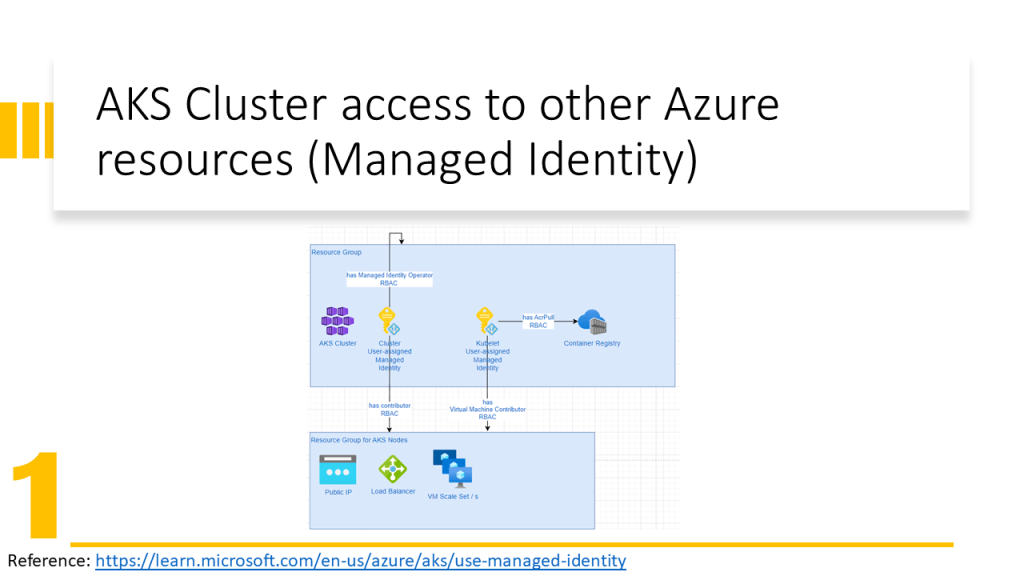
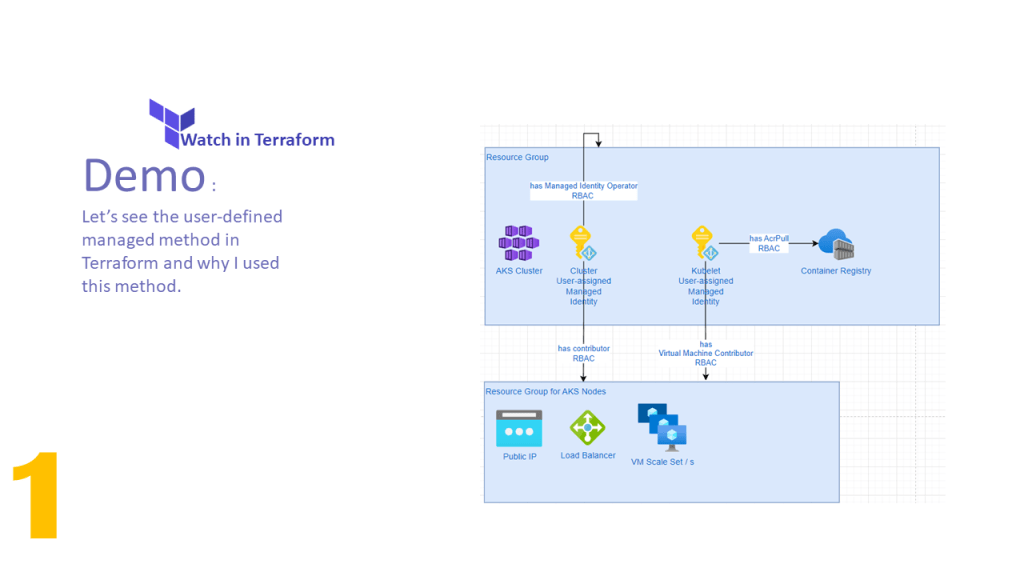
AKS Cluster needs access to other Azure resources e.g. for autoscaling must be able to expand the VM Scale Set and assign an IP Address to the VM. Therefore the AKS Cluster needs Network Contributor RBAC Role.
Kubele needs to pull images from Azure Container Registry, therefore it needs AcrPull RBAC Role.
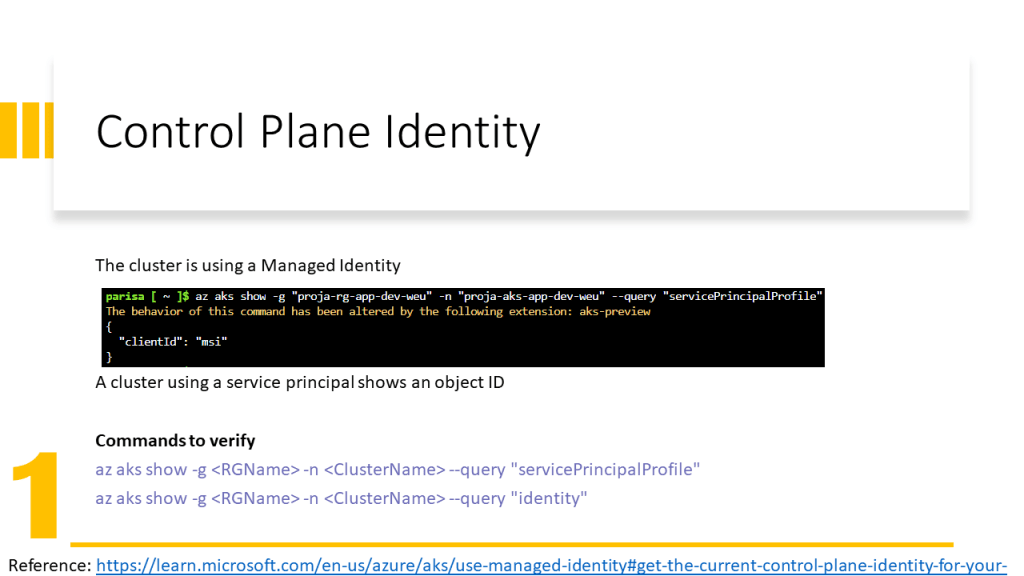
Only an identity can obtain a role. In Azure, we have two possibilities:
- Associate a Service Principal to a Service (old solution in 2022) and give RBAC roles to the service principal.
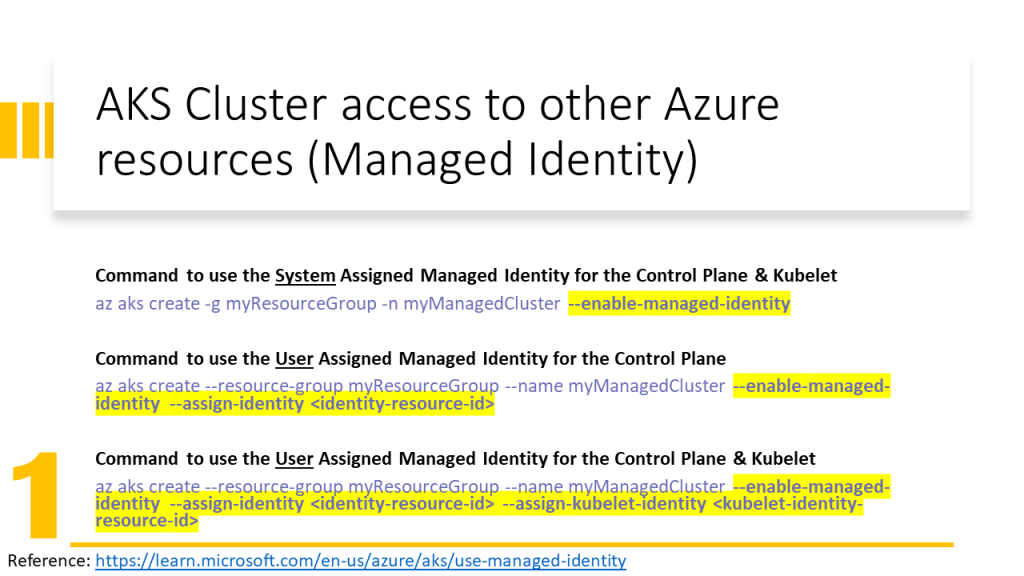
- Assign an identity to a service (new solution in 2022) and give RBAC roles to this identity. Here we have two types of identities:
- System Managed Identity: is created automatically and assigned to a service and is deleted when the service is deleted
- User Managed Identity: is created by the user and the user should assign it to a service and is not deleted when the service is deleted.
In this video, I have explained how to configure the Terraform implementation to assign the User Managed Identity to AKS Cluster and Kubelet. In addition, has been explained how to assign RBAC roles to them and which RBAC role for which purpose should be assigned.
The PowerPoint slides of the video are available here.
Shared slides: https://www.slideshare.net/parisamoosavinezhad/aks-scurity-cluster-kubelet-access-to-services
GitHub: https://github.com/ParisaMousavi/enterprise-aks/tree/2022.10.24