Software Design Patterns
Microservices Design Patterns
Database-per-Service
Domain Driven
Enterprise and industry solutions
Database-per-Service
Domain Driven
Knows as Rate Limiting. We place a throttle in front of the target service or process to control control the rate of the invocations or data flow into the target.
We can use the cloud services to apply this design pattern. This can be useful if we have an old system and we don’t want to change the code.
On each cloud vendor we have a service which does the throttling for us.
Note: It you have to handle long-running tasks, use queue, or batch.
They are used together and in combination. They affect the system architecture in great measure. Think about them in the early phase of the application design.
The security in “Bring Your Enterprise on Cloud” topic is a very hug job. But it’s implementation is not impossible. This topic is based on the related links.
The conceptual check list for security is as follows
These are the topics, which must be considered in “Bring Your Enterprise on Cloud” topic. In the following links I’ll provide an exact check list based on cloud provider.
To make the job easier it’s better to go through the conceptual check list in a layered way as demonstrated in the sample below. This can help to do the job Agile.
Layer 1: We explain how should be e.g. the network.
Layer 2: We explain how we can have e.g. a resilient network (we decide which platform service or a 3th party service or tool can to realize it)
Layer 3: We explain how we can have e.g. a high available network (we decide which platform service or a 3th party service or tool can to realize it)
Layer 4: We can add layers if we need more
Network
Resilient
High Available
Key/ Secret management
Resilient
High Available
Identity & Access Management
Resilient
High Available
Azure
Key-Vault
Key-Vault managed HSM
Dedicated HSM
AWS
Secret Manager
Certificate Manager
CloudHSM
Key Management Service (KMS)
GCP
IBM
| Azure | AWS | GCP | IBM |
|---|---|---|---|
| FIPS 140-2 level 3 | FIPS 140-2 level 3 | ||
| Single tenant | Single tenant |

Topics
Related topics
To manage and safe guard the credentials. What are the credentials?
There available services on Azure are as follows:
For more info refer to COMPUTER SECURITY RESOURCE CENTER.
| Managed | Dedicated |
|---|---|
| | |
| Security Domain (It’s the disaster recovery solution) | Doesn’t need |
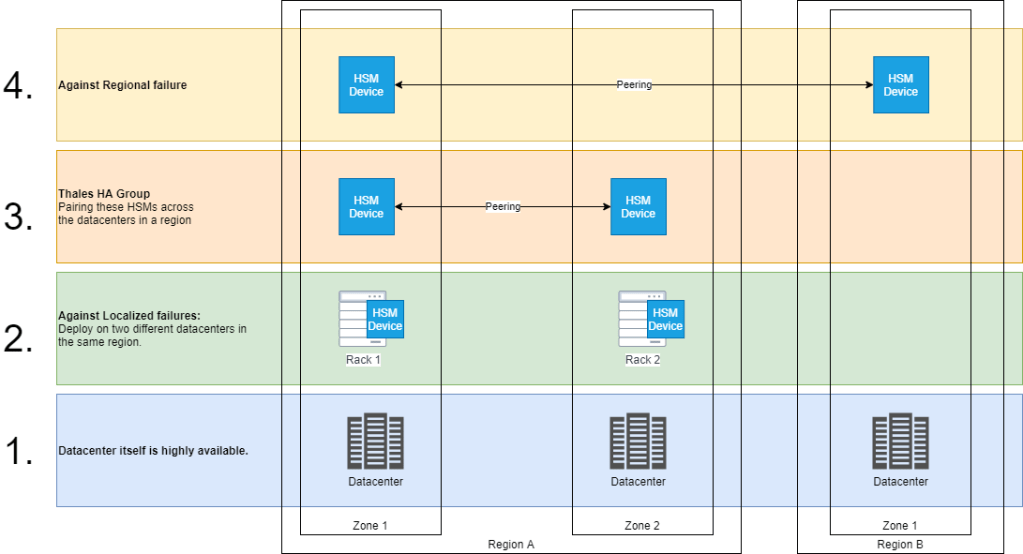
The following features provide the availability & disaster recovery requirements:
We cannot generalize a migration way to the cloud for all the companies & enterprises. But I have provided a check list of topics which can help to have a good start without wasting the time with staring from scratch.
4. Create a workspace (by clicking on create one now)
5. Select the type of the workspace (CLI-driven workflow)
6. Give a name to the workspace.
7. Create the workspace.
8. After creation the workspace the following page is appeared.

9. Set the terraform version in workspace > Setting > General and save settings.

10. Change execution mode to local (to run Terraform commands from the workstation with local variables.)

11. Pay attention: you see two settings on the page.

12. For changing the Plan & Billing go to the Organization setting.
We can use remote state to avoid saving the terraform state file locally and safe keeping the terraform state.
In doesn’t make difference which cloud vendor you have chosen as the platform. All of them follow the shared responsibility model.
What does it mean?
It means the cloud provider has the security responsibility of the cloud and cloud customer has the security responsibility in the cloud.
| Azure | AWS | GCP | IBM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shared responsibility model | Shared responsibility model | Shared responsibility model | Shared responsibility model |
What is customer responsible for?
Who should take care of security?
In companies where they up and run services/application on the cloud, the responsible teams have to have enough knowledge about the security on the cloud.
| Developers and Enterprise architect | Ensure cloud services they use are designed and deployed with security. |
| DevOps and SRE Teams | Ensure security introduced into the infrastructure build pipeline and the environments remain secure post-production. |
| InfoSec Team | Secure systems |
In which step of the project the security have to be applied?


Topics
Managing cloud spend is one of the major challenges facing experienced IT organizations today. We must be able to do the following taks in a best way.
To do the tasks above we have the following possibilities in aws:
An accurate cost estimation that meets and exceeds your organization’s budgetary goals requires you to ask important questions, interpret data, and implement AWS best practices [Source].
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| 11 9’s guarantee | 99.999999999% durability of objects over a given year. This durability level corresponds to an average annual expected loss of 0.000000001% of objects |
| AWS Support | Paid support plans offering AWS customers access to AWS technical experts and professional guidance |
| Durability | The probability that the object will remain intact and accessible after a period of one year |
| Fault Tolerance | The property that enables a system to continue operating properly in the event of the failure of (or one or more faults within) some of its components |
| High Availability | Refers to systems that are durable and likely to operate continuously without failure for a long time |
| Memory-Optimized | The R3 instance class recommended for applications that require high memory performance |
| Storage-Optimized | Instances are designed for workloads that require high, sequential read and write access to very large data sets on local storage. They are optimized to deliver tens of thousands of low-latency, random I/O operations per second (IOPS) to applications |
you only pay for services you use, and once you stop using them, AWS stops charging you immediately and doesn’t levy any termination fees.
There is no cost for uploading data into the AWS cloud, although you will pay for storage and data transfer back out. Because of the massive scale of the AWS technology platform, there is no limit to how much data you can upload.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Availability Zones | A logical data center in an AWS region with redundant and separate power, networking and connectivity reducing the likelihood of two zones failing simultaneously |
| AWS CloudFront | Fast content delivery network (CDN) service that securely delivers data, videos, applications, and APIs to customers globally with low latency |
| AWS Local Zones | A type of AWS infrastructure deployment that places AWS compute, storage, database, and other select services closer to large population, industry, and IT centers where no AWS Region exists today |
| AWS Regions | A geographical location with a collection of availability zones physically isolated from and independent of every other region |
| Edge Location | A physical site that CloudFront uses to cache copies of your content for faster delivery to users at any location |
| Points of Presence | AWS Edge Locations and Regional Edge Caches used for both AWS CloudFront and Lambda@Edge to deliver content to end users at high speeds |
| VPC Peering | A networking connection between two AWS VPCs that allows you to route traffic between them using private IP addresses |
| VPC Sharing | allows you to share subnets with other AWS accounts in your organization |

You owe your dreams your courage.
Koleka Putuma

The following words and descriptions are the wording we should know in the field of autonomous driving.
| Description | |
|---|---|
| LSTM | Long short-term memory |
| RNN | |
| FCN | |
| GRU | |
| NLP | |
| Multicore | |
| Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) | |